Strategic HR: The Secret Ingredient to Sustainable Business Excellence
The strategic contribution of Human Resource (HR) organizations to a company’s success is multifaceted and can significantly influence overall performance, competitiveness, and sustainability.
While it might depend on the company situation here are some of the key areas where HR can strategically contribute to:
- Talent Acquisition and Management: HR plays a crucial role in attracting, selecting, and retaining the right talent that aligns with the company’s strategic goals. Through effective recruitment strategies, HR ensures the organization has the human capital necessary for success. Especially for startups and fast growing company this can be a game changer.
- Training and Development: HR is responsible for identifying skill gaps and developing programs to enhance the skills and competencies of employees. This not only helps in achieving the current objectives but also prepares the organization for future challenges.
- Performance Management: By establishing clear performance standards and evaluating employee performance regularly, HR ensures that the company’s objectives are met efficiently. This process also identifies high performers and areas where improvements are needed.
- Employee Engagement: HR strategies that improve job satisfaction and employee engagement can lead to higher productivity, better customer service, and reduced turnover rates. Engaged employees are more likely to contribute positively to the company’s goals.
- Workforce Planning and Development: HR’s strategic planning includes forecasting the company’s future talent needs and developing a plan to meet those needs. This involves understanding the changing market dynamics and aligning the workforce accordingly.
- Compensation and Benefits: Strategically designed compensation and benefits packages not only help in attracting and retaining talent but also motivate employees to perform at their best. HR ensures that the compensation structure is competitive and aligns with the organization’s financial capabilities and strategic objectives.
- Organizational Culture and Change Management: HR plays a pivotal role in shaping the company’s culture and leading change management initiatives. A positive organizational culture enhances employee loyalty and productivity, while effective change management ensures the organization can navigate through transitions smoothly.
- Compliance and Risk Management: HR ensures that the company complies with all labor laws and regulations, reducing legal risks and protecting the company’s reputation. This includes managing ethical practices, diversity, and inclusion efforts.
- Strategic HR Planning: HR contributes to the formulation of the business strategy by providing insights into the capabilities and limitations of the company’s workforce. This ensures that the human capital strategy is fully integrated with the business strategy.
Technology and Innovation: HR can drive innovation by promoting a culture of continuous learning and by implementing the latest HR technologies for better efficiency and decision-making. This includes leveraging data analytics for talent management, performance tracking, and predictive analytics.
 In essence, the strategic contribution of HR organizations goes beyond traditional administrative functions to play a critical role in guiding and implementing strategies that enhance the company’s ability to achieve its long-term goals. By effectively managing the organization’s most valuable asset—its people—HR can significantly influence the company’s success.
In essence, the strategic contribution of HR organizations goes beyond traditional administrative functions to play a critical role in guiding and implementing strategies that enhance the company’s ability to achieve its long-term goals. By effectively managing the organization’s most valuable asset—its people—HR can significantly influence the company’s success.
Measuring and benchmarking the strategic contributions of Human Resources (HR) to company success involves a blend of qualitative and quantitative metrics. While there is no one-size-fits-all methodology, organizations often use a mix of industry standards, best practices, and customized metrics that align with their strategic goals. Here’s how the contribution in each area can be measured and/or benchmarked:
Key Areas | Metrics | Benchmarking Strategies |
|---|---|---|
Talent Acquisition and Management |
|
|
Training and Development |
|
|
Performance Management |
|
|
Employee Engagement |
|
|
Workforce Planning and Development |
|
|
Compensation and Benefits |
|
|
Organizational Culture and Change Management |
|
|
Compliance and Risk Management |
|
|
Strategic HR Planning |
|
|
Technology and Innovation |
|
|
This table provides a structured overview of how the strategic contributions of HR can be measured and benchmarked. Keep in mind that the choice of metrics and benchmarking strategies should be tailored to the specific context, goals, and industry of the organization.
HR Strategic Contribution Assessment Example
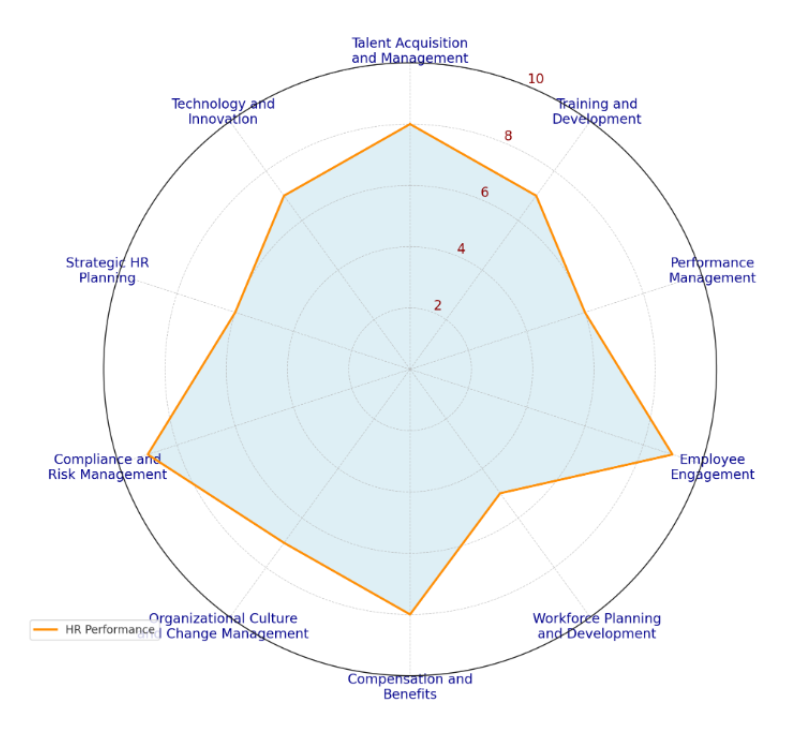
Standard methodologies for benchmarking HR contributions include:
- Balanced Scorecard: A strategic planning and management system used to align business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization, improve internal and external communications, and monitor organization performance against strategic goals.
- HR Scorecard: Adapts the Balanced Scorecard concept specifically for HR, focusing on measuring HR’s impact on business performance through defined HR processes and systems.
- Benchmarking Studies: Conducting or participating in industry-specific benchmarking studies to compare HR practices and outcomes against those of peers and competitors.
- Surveys and Feedback Tools: Using employee engagement surveys, exit interviews, and other feedback mechanisms to gather insights on HR initiatives and their impact.
No single methodology can capture the full spectrum of HR’s strategic contributions, so organizations should develop a customized approach that aligns with their unique business context, goals, and industry benchmarks.
For a comprehensive and insightful analysis, we recommend the following multi-faceted approach as a first step: Conduct a detailed survey across various stakeholder groups within the organization, including the CEO, Executives, the Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO), HR team members, general employees, and, if feasible, former employees. The survey should be designed to gather two crucial pieces of information from each group:
- Importance Assessment: Ask participants to rate the importance they attribute to each strategic HR area. This will help in understanding the perceived value and priority of different HR functions across the organizational hierarchy and workforce.
- Performance Evaluation: Request participants to provide a performance rating for the HR department in each of these strategic areas.
This dual-faceted approach aims to capture a holistic view of both the desired importance of various HR functions (as seen by different internal stakeholders) and their perceptions of how well the HR department is performing in those areas. Analyzing the data collected from these diverse perspectives will offer a rich, internal viewpoint on where the HR department stands in terms of meeting the organization’s expectations and needs. Additionally, it will highlight areas of strategic alignment or misalignment, revealing opportunities for targeted improvements and adjustments in HR strategies to better serve the organizational goals and employee needs.
Internal assessors may have biases or blind spots that could affect the objectivity of the assessment while external companies can offer an impartial perspective, potentially identifying issues that internal teams might overlook. A hybrid approach, utilizing both internal and external resources, can sometimes offer the best of both worlds—leveraging internal insights and engagement while benefiting from the objectivity and expertise of external consultants especially when it comes to benchmarking. This might involve using an external company to conduct the initial assessment and benchmarking, followed by internal teams taking on the implementation of recommendations with ongoing external support as needed.
Go To’s: CEOs and CHROs should prioritize strategic alignment between HR initiatives and business objectives, invest in HR analytics for informed decision-making, foster a culture of continuous learning and innovation, and embrace technology to enhance HR efficiency. Engaging external expertise for unbiased insights while ensuring internal stakeholder involvement is crucial for holistic HR strategy development.


