Aligning Strategy with Geography: Picking the Optimal Country for Your GCC
The Global GCC Dilemma: Finding the Ideal Country for Talent, Cost, and Culture
 Choosing the right country for a Global Competence Center (GCC) is not just a decision; it’s a strategic masterstroke that can propel a company’s global capabilities or stifle its ambitions.
Choosing the right country for a Global Competence Center (GCC) is not just a decision; it’s a strategic masterstroke that can propel a company’s global capabilities or stifle its ambitions.
While Operation Centers of Excellence (OCEs) offer localized expertise, GCCs are all about global integration—leveraging talent, technology, and innovation on a worldwide scale. In this article, we dive deep into the strengths and weaknesses of leading GCC destinations like India, Poland, the Philippines, and Mexico. We explore where the best tech talent resides, who dominates in customer service, and which regions offer multilingual powerhouses.
But it’s not all smooth sailing: we also unpack the challenges CTOs face, from navigating internal politics and cultural alignment to overcoming infrastructure issues and talent gaps.
Curious to find out which country aligns with your strategic vision? Whether you’re eyeing a hub for tech, R&D, or customer service, this guide will help you balance cost, talent, and cultural fit to make your GCC a success. Dive in and discover the roadmap for making a decision that can transform your company’s future.
Understanding the Difference: GCCs vs. OCEs
Before selecting a country, it’s important to understand the fundamental difference between a Global Competence Center and an Operation Center of Excellence.
Operation Centers of Excellence (OCEs) typically focus on specialized, localized expertise. They are designed to support a specific area or regional operations, offering services that align closely with the local market needs. Think of OCEs as the “special forces” within a company: highly skilled in one region or function, but not necessarily built for global integration.
Global Competence Centers (GCCs), on the other hand, are centralized hubs that coordinate operations, share knowledge, and streamline processes on a global scale. They support multiple regions and are set up to leverage economies of scale, centralized technology, and shared resources to optimize global functions like IT, finance, R&D, and customer service.
The Choice: OCEs are best when localized expertise is crucial. GCCs are better suited for organizations aiming for unified global efficiency and innovation.
Estimated Market Size Overview
As of recent years, the Global Competence Center (GCC) market is estimated to be substantial and growing, with significant contributions from several key countries, especially in emerging markets known for their cost-effective, skilled workforces.
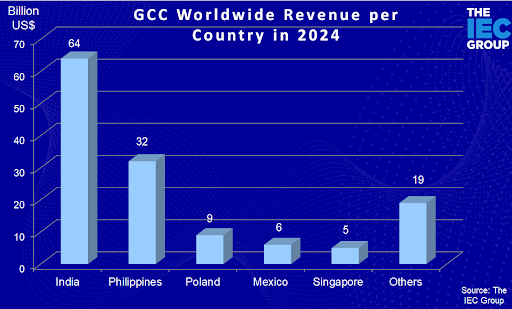
Global Market Size: The GCC market was projected to exceed $135 billion globally in 2024, with an expected annual growth rate of about 10-15% due to increased adoption by multinational companies.
Key Country-Specific GCC Markets
- India: India remains the largest GCC hub, with estimates suggesting it hosts over 1,700 GCCs as of 2024 and a contribution over $64 billion annually, driven by sectors such as IT, finance, and R&D.
- The Philippines: The Philippines is a significant player, particularly in customer service and back-office functions, contributing approximately $32 billion annually. Driven by cost efficiencies and skilled English-speaking talent, the GCC sector in the Philippines has a projected annual growth rate of 12%.
- Poland: Poland is a growing GCC destination in Europe, especially for financial services and IT support. The sector’s market value is estimated at $8-10 billion annually.
- Mexico: Mexico’s proximity to the U.S. has made it a popular location for North American companies, contributing an estimated $5-7 billion to the GCC market.The country focuses on customer service, logistics, and some manufacturing-related GCCs.
- Singapore: Singapore is a high-value GCC hub, especially for APAC headquarters, finance, and R&D. The sector’s market value is around $4-6 billion annually. With a focus on innovation and high-skill sectors, Singapore’s GCCs continue to see demand from tech and pharmaceutical industries.
These figures highlight a few key players, but as the demand for GCCs grows, other countries like Brazil, Malaysia, and South Africa are also emerging as competitive locations. The growth trend for GCCs globally is expected to stay strong, as companies seek cost savings, talent access, and centralized expertise.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Popular GCC Locations
- India: The Veteran Hub
Strengths:
- Talent Pool: India boasts one of the largest, highly skilled workforces in the world, particularly in IT, software development, and customer service. Cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad, and Pune are known for their tech-savvy populations.
- Cost Efficiency: Labor costs in India are substantially lower compared to Western countries, offering significant savings.
- Established Ecosystem: India has a mature outsourcing industry with existing infrastructure that supports GCC operations.
Weaknesses:
- Infrastructure: While improving, challenges with power stability and transport infrastructure can impact operations.
- Attrition Rates: High employee turnover in competitive job markets can disrupt GCC stability.
- Regulatory Complexity: Compliance with local labor laws and data privacy regulations can be more complicated than in some other countries.
Cultural Alignment: Indian professionals are known for their adaptability and English proficiency, making cultural alignment easier for Western companies. However, communication styles may vary, and time zone differences can affect collaboration with teams in Europe and the Americas.
- Poland: The European Tech Powerhouse
Strengths:
- Highly Skilled Workforce: Poland is home to a large number of IT and engineering graduates, making it ideal for tech-focused GCCs.
- EU Integration: As a member of the European Union, Poland follows EU regulations, making it easier for companies with European operations to comply with regional laws.
- Language Skills: High proficiency in multiple European languages, especially English, German, and French.
Weaknesses:
- Cost Compared to Asia: Labor costs, while lower than Western Europe, are higher than in Asian countries like India or the Philippines.
- Talent Competition: The tech talent in Poland is in high demand, leading to potential recruitment challenges and higher wages for top-tier talent.
Cultural Alignment: Culturally, Poland aligns well with Western Europe and the U.S., making collaboration seamless. However, decision-making in Poland can be more formal, which may differ from the fast-paced, informal style of startups or tech firms in the U.S.
- The Philippines: The Service-Oriented Star
Strengths:
- Customer Service Excellence: The Philippines is globally recognized for its strong customer service sector, making it a popular choice for GCCs focused on customer interaction.
- Language Proficiency: High English fluency is a significant advantage for companies based in English-speaking regions.
- Cultural Affinity: Filipino professionals often adapt well to Western business practices, fostering smoother integration.
Weaknesses:
- Infrastructure: While major cities like Manila and Cebu are well-developed, infrastructure in other areas can lag, impacting scalability.
- Economic Stability: Economic volatility and political changes can affect long-term investment planning.
Cultural Alignment: Filipinos have a strong sense of adaptability and hospitality, aligning well with customer-facing roles. However, hierarchical business structures can sometimes slow down decision-making processes compared to more egalitarian Western cultures.
- Mexico: The Nearshore Innovator
Strengths:
- Proximity to the U.S.: Mexico offers significant advantages for North American companies, including similar time zones and ease of travel.
- Diverse Talent: Mexico’s talent pool is expanding, especially in tech, finance, and engineering.
- Cost Advantage: Lower labor costs compared to the U.S. make it an attractive option for cost-conscious companies.
Weaknesses:
- Limited High-Skill Talent: While growing, the availability of highly specialized tech talent can be limited compared to regions like Eastern Europe or India.
- Security Concerns: Safety and security can be an issue in certain areas, which may impact employee satisfaction and retention.
Cultural Alignment: Mexican culture values strong interpersonal relationships and teamwork, aligning well with collaborative business environments. However, indirect communication styles may require adjustments for companies used to more direct approaches.
GCC World Wide Revenue and Growth
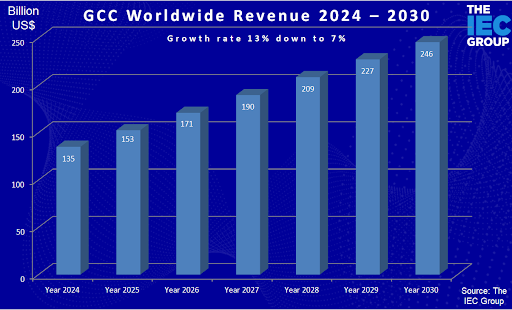
The global market for Global Competence Centers (GCCs) continues to showcase its transformative impact on multinational corporations, with the numbers speaking volumes. According to The ICE Group, the GCC market is projected to experience remarkable growth, expanding from $135 billion in 2024 to an impressive $246 billion by 2030. This trajectory underscores the increasing reliance on GCCs as strategic hubs for efficiency, innovation, and talent centralization.
A Changing Growth Landscape
The growth story, however, is not linear. The market’s annual growth rate, initially as high as 13%, is expected to gradually taper off to a more sustainable 7% by 2030. This shift reflects a natural evolution: as GCC adoption becomes widespread, the market is transitioning from a phase of rapid expansion to one of relative maturity.
Key Drivers of Growth
- Increased Adoption Across Industries:
- Tech giants and pharmaceutical companies are leading the charge, leveraging GCCs to accelerate R&D and improve operational efficiency.
- Emerging sectors like Fintech and Green Technology are driving additional demand, recognizing GCCs as critical enablers for scalability.
- Global Integration of Advanced Technologies:
- Hyper-automation, AI, and machine learning are boosting the capabilities of GCCs, further enticing companies to invest in centralized operations.
- Enhanced cybersecurity measures and unified data management frameworks are making GCCs indispensable in regulated industries.
- Cost Optimization and Talent Access:
- Companies are flocking to regions like India, Poland, and the Philippines to tap into affordable, highly skilled workforces.
- The rising emphasis on reducing compliance risks and improving customer satisfaction is further fueling the expansion.
The Saturation Signal
As the growth rate moderates, the GCC market’s slight deceleration highlights increasing market saturation. Companies that have already established robust GCC frameworks are focusing on optimizing their existing operations rather than expanding into new ones. This trend suggests a maturation of the market, with incremental innovation and efficiency improvements driving future gains.
Opportunities Amid Moderation
Despite the slowing growth, the GCC market remains fertile ground for innovation:
- Niche GCCs: Companies are shifting towards specialized GCCs tailored for functions like AI development, green R&D, and advanced cybersecurity.
- Regional Expansion: Growth in less saturated regions, such as Africa and South America, presents untapped potential.
- Collaborative GCC Ecosystems: Companies are exploring partnerships to leverage shared infrastructure and resources, boosting cost-efficiency.
The market may be maturing, but its role as a cornerstone of global operations remains unshaken. From driving cost savings to spearheading innovation, GCCs are poised to continue reshaping the way multinational corporations operate in an increasingly interconnected world.
Exploring Talent Opportunities
One of the main drivers for selecting a country for a GCC is the availability of talent. Here’s how different regions stack up:
- Tech Talent: India and Poland lead in this category. India’s vast pool of IT professionals and engineers, combined with Poland’s strong educational focus on technology, makes them both top choices for tech-heavy GCCs.
- Customer Service: The Philippines stands out as the best option, thanks to its established call center industry and high levels of English fluency.
- Engineering and R&D: Eastern Europe, including Poland and the Czech Republic, is known for producing skilled engineers, making it an attractive location for R&D-focused GCCs.
- Multilingual Capabilities: If a company needs a multilingual GCC, Poland and Mexico provide solid options, with professionals skilled in multiple European languages and Spanish, respectively.
Cultural Alignment: Why It Matters
Cultural alignment is often an overlooked aspect of choosing a GCC location, but it can have significant implications for productivity and employee satisfaction. For example:
- Communication Styles: Direct versus indirect communication can impact project timelines and collaboration. Western companies used to direct feedback may need to adapt when working in countries where communication is more nuanced, such as in the Philippines or India.
- Work Ethic and Hierarchies: Understanding local attitudes toward hierarchy and authority can influence how management structures a team. For instance, India and the Philippines tend to have more hierarchical business cultures, whereas Poland leans toward a more egalitarian approach.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Countries like Mexico and the Philippines are known for their adaptability, making them ideal for customer-facing roles where flexibility is key.
Challenges for CTOs in Setting Up GCCs
While selecting the best country is critical, CTOs face several challenges, both internal and external:
- Resistance to Change
- Internal Politics: Establishing a GCC can create tension within existing regional offices that may feel their roles are being diminished. CTOs must navigate this by emphasizing the complementary nature of GCCs and ensuring existing teams see the value in centralized support.
- Employee Pushback: In regions with less familiarity with automation or global operations, employees may resist new processes due to job security concerns.
- Talent Gaps
- High Demand: In popular regions like Poland and India, competition for top talent can be fierce, driving up wages and complicating recruitment efforts.
- Reskilling Needs: CTOs often need to invest in upskilling local talent to meet the specialized needs of the GCC, which can require partnerships with local universities or training providers like Udacity and Coursera.
- Infrastructure and Stability
- Variable Infrastructure: Some regions, while strong in talent, may lack the infrastructure necessary for seamless operations, which can impact service delivery and employee satisfaction.
- Economic and Political Factors: Economic volatility or political instability can make long-term planning more difficult, particularly in emerging markets.
The Final Decision: Weighing Strengths and Weaknesses
Selecting a country for a GCC is a multifaceted decision that requires balancing talent availability, cost, cultural alignment, and strategic goals. For tech-focused GCCs, India and Poland often emerge as top choices. For customer service and multilingual capabilities, the Philippines and Mexico offer strong prospects.
CTOs must conduct thorough due diligence, involving cross-departmental teams to assess needs and align on priorities. By understanding the unique strengths and challenges of different regions, CTOs can position their GCCs for success—creating not just operational centers, but global powerhouses that drive efficiency and innovation.
In this global game of chess, choosing the right country isn’t just a move; it’s a strategy that sets the tone for future growth.
CHRO Go To’s: Comprehensive Go-To’s for the CHRO on Selecting the Right Country for a Global Competence Center (GCC):
- Align with Company Strategy and Long-Term Goals:
- Ensure that the location choice aligns with the company’s strategic objectives, such as cost reduction, talent enhancement, innovation, or market expansion.
- Evaluate how the GCC can support the company’s future direction, such as scaling operations, entering new markets, or fostering R&D capabilities.
- Reflect the Company Culture:
- Choose a location where the local work culture is compatible with the company’s values and management style. This ensures smoother integration and a cohesive company culture across regions.
- Consider the impact of cultural alignment on employee engagement, leadership styles, and team collaboration.
- Determine Strategic Purpose (Cost Reduction vs. Talent Improvement):
- Clarify whether the primary objective of the GCC is to reduce operational costs or enhance the talent pool with specialized skills. This will influence country selection and help prioritize aspects like labor costs versus skill availability.
- Balance these objectives to ensure the GCC meets both immediate and long-term company needs.
- Evaluate Business Process Integration:
- Analyze how the business processes of the selected country will integrate with existing global workflows. Consider the adaptability of local teams to align with global processes and company standards.
- Plan for seamless process integration that supports the overall business strategy and promotes collaboration with other company units.
- Consider Time Zones for Optimal Collaboration:
- Select a location that allows for real-time collaboration with key company offices and stakeholders. Proximity to time zones that align with major markets or headquarters is crucial for efficient project management and communication.
- Balance time zone differences to minimize operational lags and ensure prompt service delivery.
- Understand Proximity to Internal and External Customers:
- Choose a location that positions the GCC close to your largest customer base, whether internal business units or external clients. This will improve responsiveness and client engagement.
- Evaluate the strategic advantage of being near high-demand markets for faster service and market adaptability.
- Plan for Management and Leadership Structure:
- Determine how the GCC will be managed. Assess whether key leadership positions will be filled by relocating existing employees or hiring local talent.
- Identify how many core team members need to be placed at the GCC and how they perceive the location. Their willingness and readiness to relocate will impact the success of the transition.
- Engage Key Stakeholders in Location Selection:
- Consult with senior leaders and essential employees to gain their insights and buy-in for the chosen location. This engagement helps identify potential challenges and ensures alignment with company strategy.
- Assess the willingness of key personnel to move or adapt to the new location, influencing onboarding and leadership continuity.
- Map Internal and External Talent Ecosystems:
- Evaluate the local ecosystem for both recruitment and partnership opportunities, such as relationships with training institutes or professional organizations.
- Ensure the region has the resources needed to sustain talent development and reduce reliance on external hires.
- Assess Potential Business Continuity Risks:
- Analyze geopolitical stability, economic resilience, and environmental factors that may pose risks to business continuity.
- Include contingency planning as part of the decision-making process to safeguard the company’s investment.
- Measure Scalability and Future Growth Potential:
- Ensure that the selected country can support the GCC’s expansion as the company grows. Look for opportunities to scale operations and accommodate future needs.
- Plan for long-term sustainability, such as the availability of larger facilities, infrastructure upgrades, and future workforce expansion.
- Evaluate Cost of Living and Quality of Life:
- Consider the cost of living for employees who may relocate and how this impacts compensation packages and expatriate benefits.
- Factor in quality-of-life aspects, such as healthcare, housing, and work-life balance, as they affect employee satisfaction and retention.
- Plan for Employee and Family Support:
- Include relocation assistance and support for employees who will move to the GCC, including family support services, housing assistance, and integration programs.
- Address employee concerns proactively by providing detailed information about the new location, local culture, and available support systems.
- Prepare for Change Management and Integration:
- Develop a comprehensive change management plan that facilitates the smooth integration of the GCC with the rest of the organization.
- Ensure transparent communication about the GCC’s role and benefits, aligning expectations across different company units and regions.
By addressing these key factors, the CHRO can ensure that the chosen GCC location aligns with the company’s overarching strategy, meets operational and cultural needs, and positions the organization for sustainable growth and success.
Last but not Least: If you’re facing challenges and wondering how others are managing similar issues, why not join The Leadership Collective Community? It’s a peer group and webcast platform designed for leaders to exchange insights and experiences.
Introducing the IEC Knowledge Network Free Membership – Your Gateway to Seamless Access!
We are thrilled to present a new service that goes beyond the ordinary download experience. In addition to offering you the ability to download the things you love, we are delighted to introduce the IEC Knowledge Network Free Membership.
The Free Membership option grants you access to our library of articles and videos, without the need for tedious registrations for each piece of content.
The publication serves as a trusted resource to support executives in their pursuit of sustainable and successful global expansion. In addition the IEC Practitioners are available to discuss your specific challenge in more detail and to give you clear advise..
Take advantage of this valuable resource to accelerate your global expansion journey


